Summary
This RFC defines a way for dApps to deterministically generate Ethereum accounts, similar to BIP-32, out of the Ethereum signature of an Ethereum account.
Constraints
We want dApps to generate “stealth” identities for an user, which we will call Bob, connected through “Sign-in with Ethereum” with his main identity, which we will call M.
Let’s define this process by the function f(X) where X is the identity to use.
Private
We also want this process to be as private as possible, we don’t want Bob to make a transaction with his main identity, we don’t want him to make any RPC requests. This process should ideally be offline, except if using network-based connection e.g. WalletConnect. Ethereum signature is a good candidate for this as it’s offline.
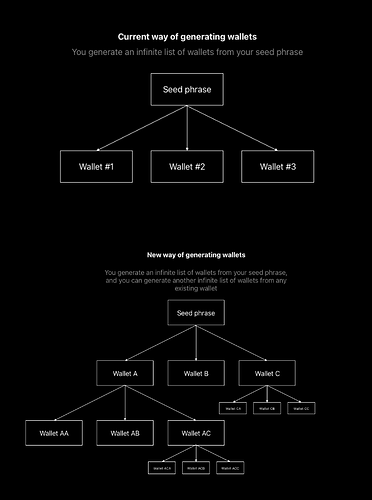
Hierarchical
We want to be able to generate multiple identities based on an index, similarly to BIP-32.
Let’s add a parameter i to the function f(X, i) for the index of such account.
Bob can generate address A = f(M, i), he can also generate address B = f(M, i + 1), without having generated A in the first place (generating B only requires M)
Deterministic
We want this process to be deterministic. If Bob goes to a dApp on his computer, generates an address A = f(M, i), then goes to the same dApp on his phone, and generate an address B = f(M, i), then both identities MUST be the same
i1 = i2 => A = B
i1 != i2 => A != B
Salted
We also want this process to be salted. The function on the dApp A will have a salt, and the function on dApp B a different salt.
Let’s add a parameter s to the function f(X, i, s)
If Bob goes to dApp A, generates an address A = f(M, x, s1), then goes to dApp B, generates an address B = g(M, x, s2), they MUST NOT be the same.
s1 = s2 => A = B
s1 != s2 => A != B
Recursive
We want the process to be recursive. Bob can generate the address AA = f(A, i, s) where A = f(M, i, s). By only having A and not M.
Defining f
With all constraints defined, we will call f a (Crypto Secure) (Private) Hierarchical Deterministic (Salted) Wallet Derivation Function, or just HDWDF
Ethereum signatures, or more specifically secp256k1 signatures are good candidates for such function
Proposal 1 with inner salt (refused)
f(wallet, index, salt) = secp256k1(sign(wallet, HMAC("Ethereum Wallet Derivation: " + index, salt)))
Where
-
HMAC can be HMAC-SHA256 or HMAC-KECCAK256; I would be in favor or SHA since it’s compatible with WebCrypto
-
sign(X, m) is the process of signing a message m with identity X, with e.g. eth_signMessage
-
secp256k1(seed) is derivating a secp256k1 curve point from a crypto secure seed, with a KDF if necessary
-
salt is a public crypto secure random value
The problem with such function is that the message to be signed is not human readable since it’s a HMAC output
Proposal 2 with outer salt (refused)
We could use HMAC outside the signature
g(wallet, index, salt) = secp256k1(HMAC(sign(wallet, "Ethereum Wallet Derivation: " + index), salt))
It has the advantage of being human readable, but the downside of being more easily craftable, a malicious dApp could make the user sign the message and then use the salt of another dApp
Proposal 3 with human-readable name (accepted)
One solution could be to use the dApp name in the message, and remove the HMAC
h(wallet, index, name) = secp256k1(sign(wallet, "Ethereum Wallet Derivation for " + name + " at index " + index))
This message could also be formatted using eth_signTypedMessage
Let me know what you think about it!